Raman Spectroscopy
Nova Elipson™ leverages Raman spectroscopy, a vibrational spectroscopy technique to detect material properties such as strain, crystallinity, phases, grain size, and composition. A non-destructive optical method, Raman spectroscopy combines small spot size and high speed to serve as the metrology of choice for the memory and logic segments.
Why Raman Spectroscopy?
The Raman spectrum provides direct information of the vibrational properties, which are highly sensitive to various material parameters. Translation of the measured spectrum into metrology parameters of interest is based on either empirical rules, model-based methods, or machine learning approaches.
Raman spectroscopy has been known for many years as a suitable lab technology for R&D needs. With Nova Elipson™, Nova has taken this technology one step further into the fab.
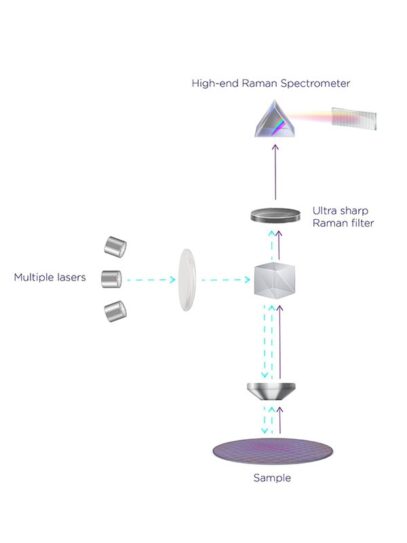
How it Works?
Raman spectroscopy relies on inelastic scattering of photons, whereby light interacts with vibrational excitations (phonons). The vibrational modes of the probed material either absorb or enhance the incident photon energy, leading to a wavelength shift of the scattered light. Nova uses Raman spectroscopy to measure the degree of the wavelength shift and interoperate it with the material’s properties.



